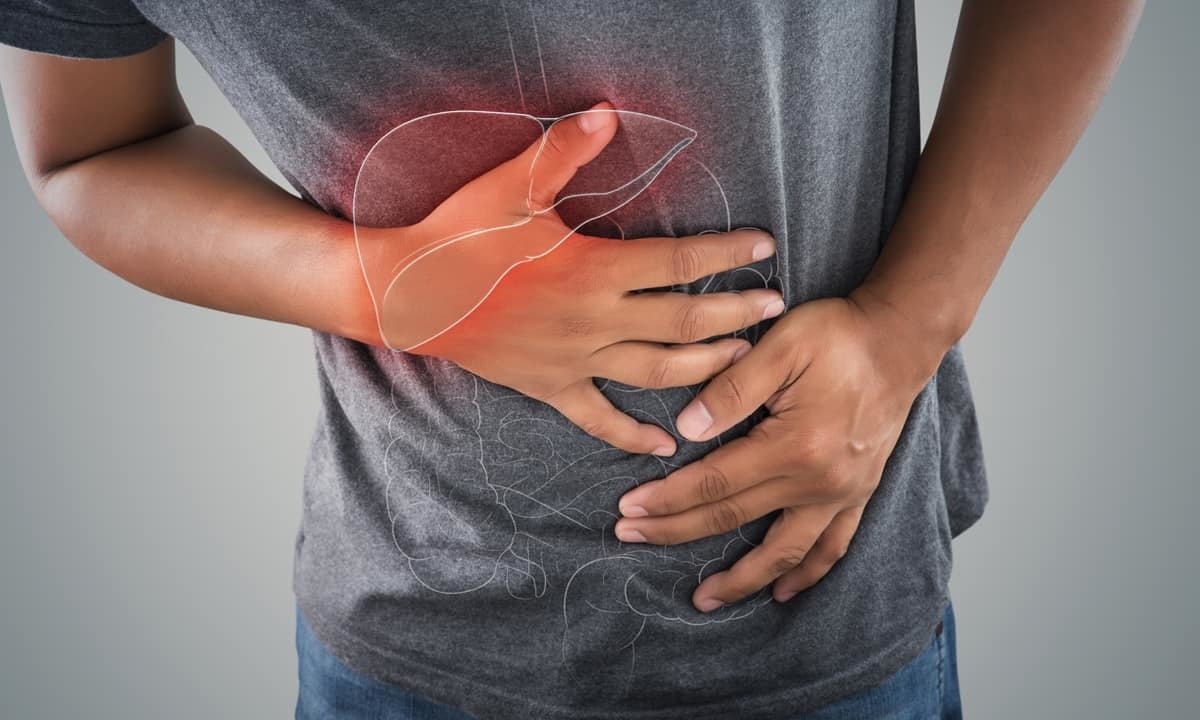
Dr. Vinit Shah, Senior consultant Hepatology (Liver Transplantation medicine and Liver diseases), Ruby Hall Clinic, Pune, Maharashtra suggests effective lifestyle changes to manage fatty liver.
1. Poor diet: Consuming a diet high in processed foods, saturated fats, sugars, and excessive calories can contribute to fatty liver. Young individuals often indulge in fast food and sugary beverages, which can exacerbate the condition.
Lifestyle change: Adopting a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help reduce fatty liver. Limiting intake of sugary and fatty foods is crucial. Incorporating more water and herbal teas instead of sugary drinks can also be beneficial.
2. Sedentary lifestyle: Lack of physical activity is closely linked to fatty liver development. Young people, especially with desk jobs or sedentary hobbies, may not engage in enough exercise to maintain a healthy metabolism.
Lifestyle change: Regular physical activity is essential. Incorporating at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise, such as brisk walking, jogging, cycling, or swimming, most days of the week can help improve liver health. Additionally, reducing sedentary behaviour by taking breaks from prolonged sitting and incorporating more movement throughout the day is beneficial.
3. Obesity: Excess body weight, particularly abdominal obesity, is a significant risk factor for fatty liver disease. Young individuals with obesity or overweight are more prone to developing fatty liver.
Lifestyle change: Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight through a combination of dietary changes and regular exercise is crucial. Aim for gradual weight loss through portion control, mindful eating, and increased physical activity.
4. Excessive alcohol consumption: While fatty liver disease is often associated with non-alcoholic causes, excessive alcohol intake can also lead to fatty liver, especially in young adults who engage in binge drinking.
Lifestyle change: Limit alcohol consumption or abstain from it altogether. For young individuals with fatty liver, it's advisable to avoid alcohol completely to prevent further liver damage.
5. Insulin resistance and diabetes: Insulin resistance, commonly associated with obesity and unhealthy lifestyle habits, can contribute to the development of fatty liver disease, particularly in individuals with type 2 diabetes.
Lifestyle change: Managing blood sugar levels through a balanced diet, regular exercise, and medication (if prescribed) is essential for individuals with insulin resistance or diabetes. Monitoring carbohydrate intake and opting for complex carbohydrates can help stabilize blood sugar levels and improve liver health.
If you want to say goodbye to your fatty liver, it's time to adopt healthy habits early on to significantly stop progression and promote overall liver health.
.gif)
.gif)





%20(600%20%C3%97%20450px)%20(600%20%C3%97%20360px)%20(500%20%C3%97%20300px)%20(448%20%C3%97%20300px).jpeg)
.jpeg)
%20(800%20%C3%97%20450px).jpeg)
%20(509%20%C3%97%20336px)%20(528%20%C3%97%20264px).jpeg)